HLA-E & Qa-1b Non-Classical MHCs
HLA-E
HLA-E is a non-classical MHC Class 1b molecule expressed ubiquitously in humans. These molecules are key players in the innate and acquired immune response.
- HLA-E is recognized by the CD92/NKG2 receptor on NK cells and the T-cell receptor (TCR) on NKT cells. CD92/NKG2 receptor recognition allows for modulation of cytotoxicity and cytokine release by NK cells1
- HLA-E molecules are involved in presentation of antigenic peptides to CD8+ T-cells through the αβ TCRs1
- HLA-E molecules present microbial-derived peptides from human viruses or bacteria1
- HLA-E molecules function as restriction elements for specific T-cell mediated responses against pathogens such as mycobacteria, the Cytomegalovirus (CMV), and the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)1
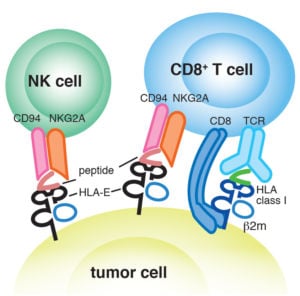
HLA-E is a key research target in combating disease conditions:
- HLA-E could potentially interact with HIV-1 gag/Capsid protein p24-derived peptide allowing HIV-1 to evade immune surveillance2
- HLA-E interacts with SARS-CoV-2 S/Spike protein S1 derived peptide on the lung epithelial cell surface leading to exhaustion of NK cells and dampening of anti-viral immune surveillance3
Two functional HLA-E alleles have been observed- HLA-E*01:01 and HLA-E*01:03.
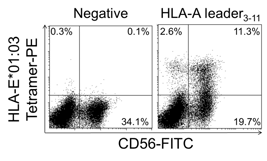
MBL International offers HLA-E tetramers comprised of human class I HLA-E*01:03 and epitope peptide derived from the HLA-A leader. The tetramer allows for detection of HLA-E*01:03-restricted HLA-A leader3-11-specific NK cells and CD8+ T cells by flow cytometry.
Qa-1b
The Qa-1b molecule is the murine non-classical MHC class 1 homolog of HLA-E. It is characterized by limited polymorphism and is similar in function to the HLA-E molecule.5
MBL International offers biotinylated Qa-1b custom monomers and tetramers available tagged with PE, APC or BV421.
Research Highlights
HLA-E and Qa-1b have been researched extensively so far in 2021.
- H Yang et al. demonstrated that invitro generation HIV-1 Gag-specific, HLA-E restricted CD8+ T cell clones was possible from naïve T-cells derived from HIV-1 negative individuals. The generated clones suppressed HIV-1 infected CD4+ target cells. This study suggests the design of a human CMV vector-based vaccine against HIV.4
- H. Vietzen et al. demonstrated that an increased frequency of the heterozygous HLA-E*0101/0103 variant was seen in patients who displayed severe COVID-19 progression as compared to the homozygous HLA-E*0101 allele. It was also shown that NKG2C-drived NK cell responses may play a key role in virus infection and COVID-19 severity.5
- X Zhang et al, have demonstrated functional cross talk between Qa-1b/HLA-E and classical TAP-dependent MHC complexes, especially in tumors that show impairment in the antigen processing machinery.6
References:
- Socié G, et al. Immune Biology of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: 19-38 (2013)
- Natterman J, et al. Antiviral Therapy 10(1): 95-107 (2005)
- Bortolotti D, et al. Cells 9(9): 1975 (2020)
- Yang H, et al. Science Immunology 6(57) (2021)
- Vietzen H, et al. Genetics in Medicine 23: 963-967 (2021)
- Zhang X, et al. Tumor Microenvironment and Immunobiology 19(6): 1076-1084 (2021)